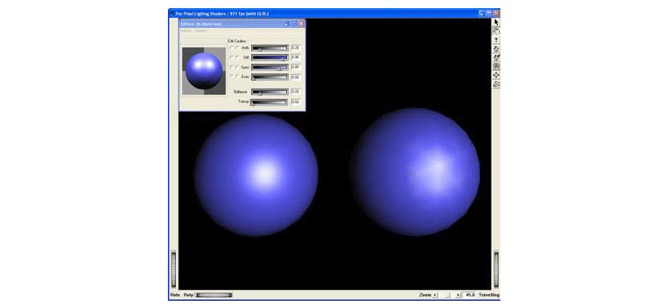
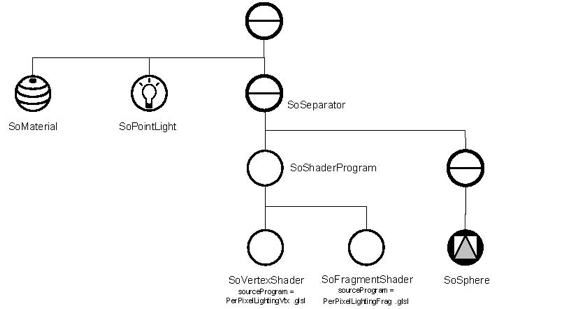
The following example computes per-pixel lighting (only the diffuse contribution is computed) on a sub-scene graph. Per-pixel lighting gives better lighting quality than per-vertex lighting (with classical OpenGL pipeline) because the light contributions are computed at each pixel instead of at each vertex.
The original example (located in $OIVHOME/src/Inventor/examples/Features/Shaders/PixelLighting), enables you to select when the application starts the shading language used for the per-pixel lighting.
The example described below, includes only the essential part of the complete source.
Example 21.1. Writing a per-pixel shader
Contents of PixelLighting.cxx
C++
void configureShaders()
{
// Initialize and set the vertex shader
VertexShader = new SoVertexShader;
// Initialize and set the fragment shader
FragmentShader = new SoFragmentShader;
// Specify the vertex and fragment shaders
VertexShader->
sourceProgram.setValue("../../../data/Shaders/PixelLightingVtx.glsl");
FragmentShader->
sourceProgram.setValue("../../../data/Shaders/PixelLightingFrag.glsl");
// Initialize and set the shader program
SoShaderProgram *shaderProgram = new SoShaderProgram;
shaderProgram->shaderObject.set1Value(0, VertexShader);
shaderProgram->shaderObject.set1Value(1, FragmentShader);
// Add the shader program to the separator
ShaderSep->insertChild(shaderProgram, 0);
}
int main(int argc, char **argv)
{
...
SoSeparator *root = new SoSeparator;
root->ref();
// Point light
PointLight = new SoPointLightManip;
ShaderSep = new SoSeparator;
SoSeparator *sphereSep = new SoSeparator;
sphereSep->addChild(new SoSphere);
// Configures the shader
configureShaders();
// Add the sphere to the shaders' separator to apply the shaders to it.
ShaderSep->addChild(sphereSep);
// Material applied to the model
SoMaterial *modelMat = new SoMaterial;
modelMat->ambientColor.setValue(0.2f, 0.2f, 0.2f);
modelMat->diffuseColor.setValue(0.3f, 0.3f, 0.9f);
modelMat->specularColor.setValue(0.6f, 0.6f, 0.8f);
modelMat->emissiveColor.setValue(0.0f, 0.0f, 0.0f);
modelMat->shininess.setValue(0.2f);
// Build the scene graph
root->addChild(modelMat);
root->addChild(PointLight);
root->addChild(ShaderSep);
...
}
.NET
void ConfigureShaders()
{
// Initialize and set the vertex shader
SoVertexShader VertexShader = new SoVertexShader();
// Initialize and set the fragment shader
SoFragmentShader FragmentShader = new SoFragmentShader();
// Specify the vertex and fragment shaders
VertexShader.sourceProgram.Value =
"$OIVNETHOME/src/Inventor/examples/data/Shaders/PixelLightingVtx.glsl";
FragmentShader.sourceProgram.Value =
"$OIVNETHOME/src/Inventor/examples/data/Shaders/PixelLightingFrag.glsl";
// Initialize and set the shader program
SoShaderProgram shaderProgram = new SoShaderProgram();
shaderProgram.shaderObject[0] = VertexShader;
shaderProgram.shaderObject[1] = FragmentShader;
// Add the shader program to the separator
ShaderSep.InsertChild(shaderProgram, 0);
}
void CreateSample()
{
...
SoSeparator root = new SoSeparator();
// Point light
SoPointLightManip PointLight = new SoPointLightManip();
ShaderSep = new SoSeparator();
SoSeparator sphereSep = new SoSeparator();
SoTranslation sphereTranslation = new SoTranslation();
sphereTranslation.translation.SetValue(3f, 0f, -2f);
sphereSep.AddChild(sphereTranslation);
sphereSep.AddChild(new SoSphere());
// Configures the shader
ConfigureShaders();
// Add the sphere to the shaders' separator to apply the shaders to it.
ShaderSep.AddChild(sphereSep);
// Material applied to the model
SoMaterial modelMat = new SoMaterial();
modelMat.ambientColor.SetValue(0.2f, 0.2f, 0.2f);
modelMat.diffuseColor.SetValue(0.3f, 0.3f, 0.9f);
modelMat.specularColor.SetValue(0.6f, 0.6f, 0.8f);
modelMat.emissiveColor.SetValue(0.0f, 0.0f, 0.0f);
modelMat.shininess.SetValue(0.2f);
// Build the scene graph
root.AddChild(modelMat);
root.AddChild(PointLight);
root.AddChild(ShaderSep);
...
}
Java
Contents of PixelLightingVtx.glsl Vertex Shader:
/* !!GLSL */
varying vec4 eposition;
varying vec3 normal;
varying vec3 diffuseColor;
varying vec3 specularColor;
varying vec3 emissiveColor;
varying vec3 ambientColor;
varying float shininess;
void main()
{
// Position in clip space
gl_Position = gl_ModelViewProjectionMatrix * gl_Vertex;
// Position in eye space
eposition = gl_ModelViewMatrix * gl_Vertex;
// Normal in eye space
normal = mat3(gl_ModelViewMatrix) * gl_Normal;
// Retrieves diffuse, specular emissive, and ambient color from the OpenGL state.
diffuseColor = vec3(gl_FrontMaterial.diffuse);
specularColor = vec3(gl_FrontMaterial.specular);
emissiveColor = vec3(gl_FrontMaterial.emission);
ambientColor = vec3(gl_FrontMaterial.ambient);
shininess = gl_FrontMaterial.shininess;
}
Contents of PixelLightingFrag.glsl fragment shader:
/* !!GLSL */
varying vec4 eposition;
varying vec3 normal;
varying vec3 diffuseColor;
varying vec3 specularColor;
varying vec3 emissiveColor;
varying vec3 ambientColor;
varying float shininess;
void main()
{
const vec3 lightColor = vec3(1, 1, 1);
const vec3 globalAmbient = vec3(0.2, 0.2, 0.2);
// Position in eye space
vec3 P = vec3(eposition);
// Normalize normal in eye space
vec3 N = normalize(normal);
// Compute the emissive term
vec3 emissive = emissiveColor;
// Compute the ambient term
vec3 ambient = ambientColor * globalAmbient;
// Compute the diffuse term
// Normalized vector toward the light source
vec3 L = normalize(vec3(gl_LightSource[0].position) - P);
float diffuseLight = max(dot(N, L), 0);
vec3 diffuse = diffuseColor * lightColor * diffuseLight;
// Compute the specular term
vec3 V = normalize(-P); // Normalized vector toward the viewpoint
vec3 H = normalize(L + V); // Normalized vector that is halfway between V and L
float specularLight = pow(max(dot(N, H),0), shininess);
if(diffuseLight <= 0)
specularLight = 0;
vec3 specular = specularColor * lightColor * specularLight;
// Define the final vertex color
gl_FragColor.xyz = emissive + ambient + diffuse + specular;
gl_FragColor.w = 1.0;
}