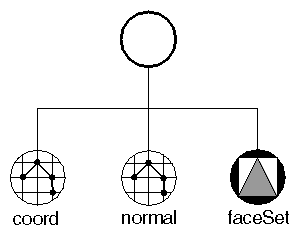
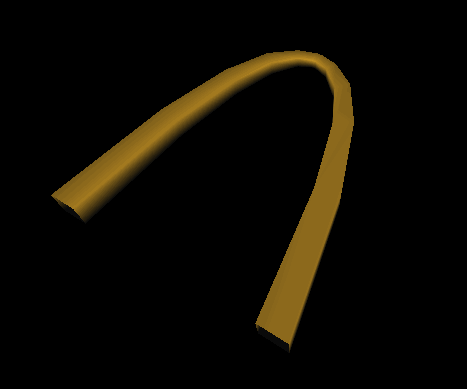Complex shapes, such as triangle strip sets and face sets, require at least a set of coordinates. If the lighting is set to PHONG, complex shapes also require a set of surface normals, as shown in Nodes Used to Create a Simple Indexed Face Set . Coordinates and normals are defined by separate nodes in the scene graph so that this information can be shared by other nodes.
Examples of complex shapes include the following:
- Face set, indexed face set
- Line set, indexed line set
- Triangle strip set, indexed triangle strip set
- Point set
- Quad mesh
- NURBS curve and surface
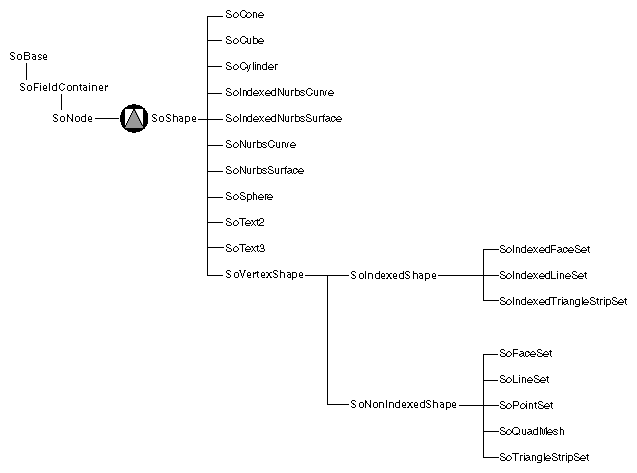
Shape-Node Classes
An SoCoordinate3 node sets the current coordinates in the rendering state to the specified points. This node contains one field (point), which is of type SoMFVec3f. For example:
C++ :
SbVec3f verts[6];
SoCoordinate3* coord = new SoCoordinate3;
// ...Initialize vertices array ...
coord->point.setValues( 0, 6, verts );
C# :
SbVec3f[] verts = new SbVec3f[6];
SoCoordinate3 coord = new SoCoordinate3();
// ...Initialize vertices array ...
coord.point.SetValues( 0, verts );
Java :
SbVec3f[] verts = new SbVec3f[6];
SoCoordinate3 coord = new SoCoordinate3();
// ...Initialize vertices array ...
coord.point.setValues( 0, verts );
An SoNormal node sets the current surface normals in the rendering state to the specified vectors. This node contains one field, vector, of type SoMFVec3f.
 Normals can also be generated automatically by Inventor, in which case you do not need an SoNormal node. See the section called “Generating Normals Automatically” for further information.
Normals can also be generated automatically by Inventor, in which case you do not need an SoNormal node. See the section called “Generating Normals Automatically” for further information.
Nodes Used to Create a Simple Indexed Face Set
Face Set
An SoFaceSet is a shape node that represents a polygonal object formed by constructing faces out of the current coordinates, current normals, current materials, and current textures. It uses the values within each node in the order they are given. (To use coordinates, normals, and materials in a different order, use the SoIndexedFaceSet node, described in the next section.)
Creating a Face Set creates an obelisk using a face set composed of eight faces. The scene graph for this example is shown in Scene Graph for Face Set Example . Ignore the normal binding node for now. This node is explained in Binding Nodes Face-Set Example shows the image created by this example.
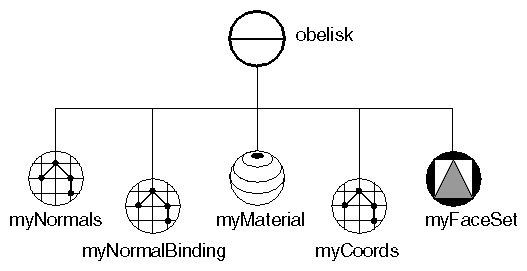
Scene Graph for Face Set Example
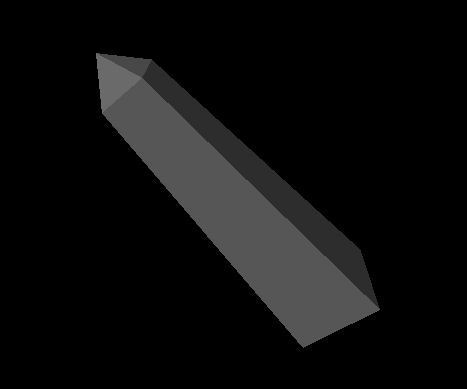
Face-Set Example
Creating a Face Set
Example : Creating a Face Set
C++ :
// Eight polygons. The first four are triangles
// The second four are quadrilaterals for the sides.
static float vertices[28][3] = {
{ 0, 30, 0 }, { -2, 27, 2 }, { 2, 27, 2 }, // front tri
{ 0, 30, 0 }, { -2, 27, -2 }, { -2, 27, 2 }, // left tri
{ 0, 30, 0 }, { 2, 27, -2 }, { -2, 27, -2 }, // rear tri
{ 0, 30, 0 }, { 2, 27, 2 }, { 2, 27, -2 }, // right tri
{ -2, 27, 2 }, { -4, 0, 4 }, { 4, 0, 4 }, { 2, 27, 2 }, // front quad
{ -2, 27, -2 }, { -4, 0, -4 }, { -4, 0, 4 }, { -2, 27, 2 }, // left quad
{ 2, 27, -2 }, { 4, 0, -4 }, { -4, 0, -4 }, { -2, 27, -2 }, // rear quad
{ 2, 27, 2 }, { 4, 0, 4 }, { 4, 0, -4 }, { 2, 27, -2 } // right quad
};
// Number of vertices in each polygon:
static long numvertices[8] = { 3, 3, 3, 3, 4, 4, 4, 4 };
// Normals for each polygon:
static float norms[8][3] = {
{ 0, .555, .832 }, { -.832, .555, 0 }, // front, left tris
{ 0, .555, -.832 }, { .832, .555, 0 }, // rear, right tris
{ 0, .0739, .9973 }, { -.9972, .0739, 0 }, // front, left quads
{ 0, .0739, -.9973 }, { .9972, .0739, 0 }, // rear, right quads
};
SoSeparator*
makeObeliskFaceSet()
{
SoSeparator* obelisk = new SoSeparator();
obelisk->ref();
// Define the normals used:
SoNormal* myNormals = new SoNormal;
myNormals->vector.setValues( 0, 8, norms );
obelisk->addChild( myNormals );
SoNormalBinding* myNormalBinding = new SoNormalBinding;
myNormalBinding->value = SoNormalBinding::PER_FACE;
obelisk->addChild( myNormalBinding );
// Define material for obelisk
SoMaterial* myMaterial = new SoMaterial;
myMaterial->diffuseColor.setValue( .4, .4, .4 );
obelisk->addChild( myMaterial );
// Define coordinates for vertices
SoCoordinate3* myCoords = new SoCoordinate3;
myCoords->point.setValues( 0, 28, vertices );
obelisk->addChild( myCoords );
// Define the FaceSet
SoFaceSet* myFaceSet = new SoFaceSet;
myFaceSet->numVertices.setValues( 0, 8, numvertices );
obelisk->addChild( myFaceSet );
obelisk->unrefNoDelete();
return obelisk;
}
C# :
// Eight polygons. The first four are triangles
// The second four are quadrilaterals for the sides.
float[, ] vertices = new float[28, 3]{
{ 0.0f, 30.0f, 0.0f }, { -2.0f, 27.0f, 2.0f }, { 2.0f, 27.0f, 2.0f }, // front tri
{ 0.0f, 30.0f, 0.0f }, { -2.0f, 27.0f, -2.0f }, { -2.0f, 27.0f, 2.0f }, // left tri
{ 0.0f, 30.0f, 0.0f }, { 2.0f, 27.0f, -2.0f }, { -2.0f, 27.0f, -2.0f }, // rear tri
{ 0.0f, 30.0f, 0.0f }, { 2.0f, 27.0f, 2.0f }, { 2.0f, 27.0f, -2.0f }, // right tri
{ -2.0f, 27.0f, 2.0f }, { -4.0f, 0.0f, 4.0f }, { 4.0f, 0.0f, 4.0f }, { 2.0f, 27.0f, 2.0f }, // front quad
{ -2.0f, 27.0f, -2.0f }, { -4.0f, 0.0f, -4.0f }, { -4.0f, 0.0f, 4.0f }, { -2.0f, 27.0f, 2.0f }, // left quad
{ 2.0f, 27.0f, -2.0f }, { 4.0f, 0.0f, -4.0f }, { -4.0f, 0.0f, -4.0f }, { -2.0f, 27.0f, -2.0f }, // rear quad
{ 2.0f, 27.0f, 2.0f }, { 4.0f, 0.0f, 4.0f }, { 4.0f, 0.0f, -4.0f }, { 2.0f, 27.0f, -2.0f } // right quad
};
// Number of vertices in each polygon:
Int32[] numvertices = new Int32[8]{ 3, 3, 3, 3, 4, 4, 4, 4 };
// Normals for each polygon:
float[, ] norms = new float[8, 3]{
{ 0.0f, 0.555f, 0.832f }, { -0.832f, 0.555f, 0.0f }, // front, left tris
{ 0.0f, 0.555f, -0.832f }, { 0.832f, 0.555f, 0.0f }, // rear, right tris
{ 0.0f, 0.0739f, 0.9973f }, { -0.9972f, 0.0739f, 0.0f }, // front, left quads
{ 0.0f, 0.0739f, -0.9973f }, { 0.9972f, 0.0739f, 0.0f }, // rear, right quads
};
SoSeparator
MakeObeliskFaceSet()
{
SoSeparator obelisk = new SoSeparator();
// Using the new SoVertexProperty node is more efficient
SoVertexProperty myVertexProperty = new SoVertexProperty();
// Define the normals used:
myVertexProperty.normal.SetValues( 0, 8, norms );
myVertexProperty.normalBinding.Value = SoNormalBinding.Bindings.PER_FACE;
// Define material for obelisk
myVertexProperty.orderedRGBA.SetValue( new SbColor( 0.4f, 0.4f, 0.4f ).GetPackedValue() );
// Define coordinates for vertices
myVertexProperty.vertex.SetValues( 0, 28, vertices );
// Define the FaceSet
SoFaceSet myFaceSet = new SoFaceSet();
myFaceSet.numVertices.SetValues( 0, numvertices );
myFaceSet.vertexProperty.Value = myVertexProperty;
obelisk.AddChild( myFaceSet );
return obelisk;
}
Java :
// Eight polygons. The first four are triangles
// The second four are quadrilaterals for the sides.
float[][] vertices = new float[][]{
{ 0.0f, 30.0f, 0.0f }, { -2.0f, 27.0f, 2.0f }, { 2.0f, 27.0f, 2.0f }, // front tri
{ 0.0f, 30.0f, 0.0f }, { -2.0f, 27.0f, -2.0f }, { -2.0f, 27.0f, 2.0f }, // left tri
{ 0.0f, 30.0f, 0.0f }, { 2.0f, 27.0f, -2.0f }, { -2.0f, 27.0f, -2.0f }, // rear tri
{ 0.0f, 30.0f, 0.0f }, { 2.0f, 27.0f, 2.0f }, { 2.0f, 27.0f, -2.0f }, // right tri
{ -2.0f, 27.0f, 2.0f }, { -4.0f, 0.0f, 4.0f }, { 4.0f, 0.0f, 4.0f }, { 2.0f, 27.0f, 2.0f }, // front quad
{ -2.0f, 27.0f, -2.0f }, { -4.0f, 0.0f, -4.0f }, { -4.0f, 0.0f, 4.0f }, { -2.0f, 27.0f, 2.0f }, // left quad
{ 2.0f, 27.0f, -2.0f }, { 4.0f, 0.0f, -4.0f }, { -4.0f, 0.0f, -4.0f }, { -2.0f, 27.0f, -2.0f }, // rear quad
{ 2.0f, 27.0f, 2.0f }, { 4.0f, 0.0f, 4.0f }, { 4.0f, 0.0f, -4.0f }, { 2.0f, 27.0f, -2.0f } // right quad
};
// Number of vertices in each polygon:
int[] numvertices = new int[]{ 3, 3, 3, 3, 4, 4, 4, 4 };
// Normals for each polygon:
float[][] norms = new float[][]{
{ 0.0f, 0.555f, 0.832f }, { -0.832f, 0.555f, 0.0f }, // front, left tris
{ 0.0f, 0.555f, -0.832f }, { 0.832f, 0.555f, 0.0f }, // rear, right tris
{ 0.0f, 0.0739f, 0.9973f }, { -0.9972f, 0.0739f, 0.0f }, // front, left quads
{ 0.0f, 0.0739f, -0.9973f }, { 0.9972f, 0.0739f, 0.0f }, // rear, right quads
};
SoSeparator
MakeObeliskFaceSet()
{
SoSeparator obelisk = new SoSeparator();
// Using the new SoVertexProperty node is more efficient
SoVertexProperty myVertexProperty = new SoVertexProperty();
// Define the normals used:
myVertexProperty.normal.setValues( 0, norms );
myVertexProperty.normalBinding.setValue( SoNormalBinding.Bindings.PER_FACE );
// Define material for obelisk
myVertexProperty.orderedRGBA.setValue( new SbColor( 0.4f, 0.4f, 0.4f ).getPackedValue() );
// Define coordinates for vertices
myVertexProperty.vertex.setValues( 0, vertices );
// Define the FaceSet
SoFaceSet myFaceSet = new SoFaceSet();
myFaceSet.numVertices.setValues( 0, numvertices );
myFaceSet.vertexProperty.setValue( myVertexProperty );
obelisk.addChild( myFaceSet );
return obelisk;
}
 When you construct a scene graph, be sure that you have used as few nodes as possible to accomplish your goals. For example, to create a multifaceted polygonal shape, it's best to put all the coordinates for the shape into one SoCoordinate node and put the description of all the face sets into a single SoFaceSet (or SoIndexedFaceSet) node rather than using multiple nodes for each face.
When you construct a scene graph, be sure that you have used as few nodes as possible to accomplish your goals. For example, to create a multifaceted polygonal shape, it's best to put all the coordinates for the shape into one SoCoordinate node and put the description of all the face sets into a single SoFaceSet (or SoIndexedFaceSet) node rather than using multiple nodes for each face.
Indexed Face Set
An SoIndexedFaceSet node is a shape node that represents a polygonal object formed by constructing faces out of the current coordinates, using the current surface normals, current materials, and current texture. In contrast to the SoFaceSet node, this node can use those values in any order. This node class contains four fields with indices that specify the ordering:
| |
| coordIndex (SoMFLong) | contains indices into the coordinates list. These indices connect coordinates to form a set of faces. A value of SO_END_FACE_INDEX (-1) indicates the end of one face and the start of the next face. This field is always used. |
| materialIndex (SoMFLong) | contains indices into the current material(s) for the materials of the face set. This field is used only when some type of indexed material binding is specified in the SoMaterialBinding node. See Binding Nodes. |
| normalIndex (SoMFLong) | contains indices into the current normals for the vertices of the face set. This field is used only when indexed normal binding (either per vertex or per face) is specified in the SoNormalBinding node. See Binding Nodes. |
| textureCoordIndex (SoMFLong) | contains indices of the texture coordinates that are applied to the shape (see Textures). |
Be sure that the indices contained in the indexed face set can actually be found in the coordinates and normals lists, or errors will occur.
 If you use the SoShapeHints node to specify that the vertices are counterclockwise, you must specify the vertex indices according to the right-hand rule. The right-hand rule states that if you place the fingers of your right hand around the face following the direction in which the vertices are specified, your thumb points in the general direction of the geometric normal. Alternatively, you can specify the vertices in clockwise order. In this case, the direction of the geometric normal is determined by the left-hand rule.
If you use the SoShapeHints node to specify that the vertices are counterclockwise, you must specify the vertex indices according to the right-hand rule. The right-hand rule states that if you place the fingers of your right hand around the face following the direction in which the vertices are specified, your thumb points in the general direction of the geometric normal. Alternatively, you can specify the vertices in clockwise order. In this case, the direction of the geometric normal is determined by the left-hand rule.
Creating an Indexed Face Set creates the first stellation of the dodecahedron from an indexed face set. Each of the twelve intersecting faces is a pentagon. The scene graph diagram for this example is shown in Scene Graph for Indexed Face-Set Example . Indexed Face-Set Example shows the image created by this example.
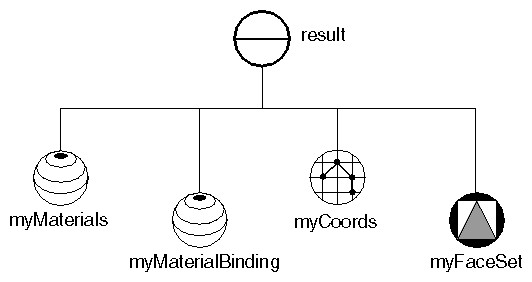
Scene Graph for Indexed Face-Set Example
Example : Creating an Indexed Face Set
C++ :
// Positions of all of the vertices:
static float vertexPositions[12][3] = {
{ 0.0000, 1.2142, 0.7453 }, // top
{ 0.0000, 1.2142, -0.7453 }, // points surrounding top
{ -1.2142, 0.7453, 0.0000 }, { -0.7453, 0.0000, 1.2142 }, { 0.7453, 0.0000, 1.2142 }, { 1.2142, 0.7453, 0.0000 },
{ 0.0000, -1.2142, 0.7453 }, // points surrounding bottom
{ -1.2142, -0.7453, 0.0000 }, { -0.7453, 0.0000, -1.2142 }, { 0.7453, 0.0000, -1.2142 }, { 1.2142, -0.7453, 0.0000 },
{ 0.0000, -1.2142, -0.7453 }, // bottom
};
C# :
// Positions of all of the vertices:
float[, ] vertexPositions = new float[12, 3]{
{ 0.0000f, 1.2142f, 0.7453f }, // top
{ 0.0000f, 1.2142f, -0.7453f }, // points surrounding top
{ -1.2142f, 0.7453f, 0.0000f }, { -0.7453f, 0.0000f, 1.2142f }, { 0.7453f, 0.0000f, 1.2142f }, { 1.2142f, 0.7453f, 0.0000f },
{ 0.0000f, -1.2142f, 0.7453f }, // points surrounding bottom
{ -1.2142f, -0.7453f, 0.0000f }, { -0.7453f, 0.0000f, -1.2142f }, { 0.7453f, 0.0000f, -1.2142f }, { 1.2142f, -0.7453f, 0.0000f },
{ 0.0000f, -1.2142f, -0.7453f }, // bottom
};
Java :
// Positions of all of the vertices:
float[][] vertexPositions = new float[][]{
{ 0.0000f, 1.2142f, 0.7453f }, // top
{ 0.0000f, 1.2142f, -0.7453f }, // points surrounding top
{ -1.2142f, 0.7453f, 0.0000f }, { -0.7453f, 0.0000f, 1.2142f }, { 0.7453f, 0.0000f, 1.2142f }, { 1.2142f, 0.7453f, 0.0000f },
{ 0.0000f, -1.2142f, 0.7453f }, // points surrounding bottom
{ -1.2142f, -0.7453f, 0.0000f }, { -0.7453f, 0.0000f, -1.2142f }, { 0.7453f, 0.0000f, -1.2142f }, { 1.2142f, -0.7453f, 0.0000f },
{ 0.0000f, -1.2142f, -0.7453f }, // bottom
};
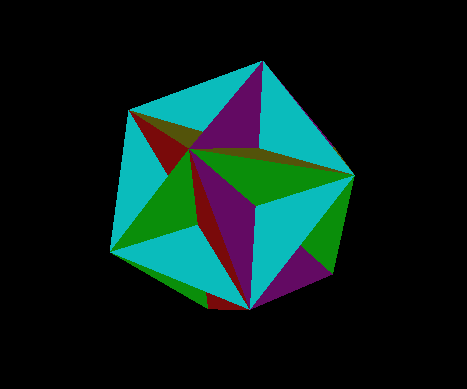
Indexed Face-Set Example
// Connectivity, information; 12 faces with 5 vertices each },
// (plus the end-of-face indicator for each face):
static long indices[72] = {
1, 2, 3, 4, 5, SO_END_FACE_INDEX, // top face
0, 1, 8, 7, 3, SO_END_FACE_INDEX, // 5 faces about top
0, 2, 7, 6, 4, SO_END_FACE_INDEX, 0, 3, 6, 10, 5, SO_END_FACE_INDEX, 0, 4, 10, 9, 1, SO_END_FACE_INDEX, 0, 5, 9, 8, 2, SO_END_FACE_INDEX,
9, 5, 4, 6, 11, SO_END_FACE_INDEX, // 5 faces about bottom
10, 4, 3, 7, 11, SO_END_FACE_INDEX, 6, 3, 2, 8, 11, SO_END_FACE_INDEX, 7, 2, 1, 9, 11, SO_END_FACE_INDEX, 8, 1, 5, 10, 11, SO_END_FACE_INDEX,
6, 7, 8, 9, 10, SO_END_FACE_INDEX, // bottom face
};
// Colors for the 12 faces
static float colors[12][3] = { { 1.0, .0, 0 }, { .0, .0, 1.0 }, { 0, .7, .7 }, { .0, 1.0, 0 }, { .7, .7, 0 }, { .7, .0, .7 },
{ 0, .0, 1.0 }, { .7, .0, .7 }, { .7, .7, 0 }, { .0, 1.0, .0 }, { 0, .7, .7 }, { 1.0, .0, 0 } };
// Routine to create a scene graph representing a dodecahedron
SoSeparator*
makeStellatedDodecahedron()
{
SoSeparator* result = new SoSeparator;
result->ref();
// Define colors for the faces
SoMaterial* myMaterials = new SoMaterial;
myMaterials->diffuseColor.setValues( 0, 12, colors );
result->addChild( myMaterials );
SoMaterialBinding* myMaterialBinding = new SoMaterialBinding;
myMaterialBinding->value = SoMaterialBinding::PER_FACE;
result->addChild( myMaterialBinding );
// Define coordinates for vertices
// Define coordinates for vertices
SoCoordinate3* myCoords = new SoCoordinate3;
myCoords->point.setValues( 0, 12, vertexPositions );
result->addChild( myCoords );
// Define the IndexedFaceSet, with indices into the vertices:
SoIndexedFaceSet* myFaceSet = new SoIndexedFaceSet;
myFaceSet->coordIndex.setValues( 0, 72, indices );
result->addChild( myFaceSet );
result->unrefNoDelete();
return result;
}
C# :
// Connectivity, information; 12 faces with 5 vertices each },
// (plus the end-of-face indicator for each face):
Int32[] indices = new Int32[72]{
1, 2, 3, 4, 5, -1, // top face
0, 1, 8, 7, 3, -1, // 5 faces about top
0, 2, 7, 6, 4, -1, 0, 3, 6, 10, 5, -1, 0, 4, 10, 9, 1, -1, 0, 5, 9, 8, 2, -1,
9, 5, 4, 6, 11, -1, // 5 faces about bottom
10, 4, 3, 7, 11, -1, 6, 3, 2, 8, 11, -1, 7, 2, 1, 9, 11, -1, 8, 1, 5, 10, 11, -1,
6, 7, 8, 9, 10, -1, // bottom face
};
// Colors for the 12 faces
float[, ] colors = new float[12, 3]{ { 1.0f, 0.0f, 0.0f }, { 0.0f, 0.0f, 1.0f }, { 0.0f, 0.7f, 0.7f }, { 0.0f, 1.0f, 0.0f },
{ 0.7f, 0.7f, 0.0f }, { 0.7f, 0.0f, 0.7f }, { 0.0f, 0.0f, 1.0f }, { 0.7f, 0.0f, 0.7f },
{ 0.7f, 0.7f, 0.0f }, { 0.0f, 1.0f, 0.0f }, { 0.0f, 0.7f, 0.7f }, { 1.0f, 0.0f, 0.0f } };
// Routine to create a scene graph representing a dodecahedron
SoSeparator
makeStellatedDodecahedron()
{
SoSeparator result = new SoSeparator();
// Using the new SoVertexProperty node is more efficient
SoVertexProperty myVertexProperty = new SoVertexProperty();
// Define colors for the faces
for ( int i = 0; i < 12; i++ )
myVertexProperty.orderedRGBA[i] = new SbColor( colors[ i, 0 ], colors[ i, 1 ], colors[ i, 2 ] ).GetPackedValue();
myVertexProperty.materialBinding.Value = SoMaterialBinding.Bindings.PER_FACE;
// Define coordinates for vertices
myVertexProperty.vertex.SetValues( 0, 12, vertexPositions );
// Define the IndexedFaceSet, with indices into
// the vertices:
SoIndexedFaceSet myFaceSet = new SoIndexedFaceSet();
myFaceSet.coordIndex.SetValues( 0, indices );
myFaceSet.vertexProperty.Value = myVertexProperty;
result.AddChild( myFaceSet );
return result;
}
Java :
// Connectivity, information; 12 faces with 5 vertices each },
//(plus the end-of-face indicator for each face):
int[] indices = new int[]{
1, 2, 3, 4, 5, -1, // top face
0, 1, 8, 7, 3, -1, // 5 faces about top
0, 2, 7, 6, 4, -1, 0, 3, 6, 10, 5, -1, 0, 4, 10, 9, 1, -1, 0, 5, 9, 8, 2, -1,
9, 5, 4, 6, 11, -1, // 5 faces about bottom
10, 4, 3, 7, 11, -1, 6, 3, 2, 8, 11, -1, 7, 2, 1, 9, 11, -1, 8, 1, 5, 10, 11, -1,
6, 7, 8, 9, 10, -1, // bottom face
};
// Colors for the 12 faces
float[][] colors =
new float[][]{ { 1.0f, 0.0f, 0.0f }, { 0.0f, 0.0f, 1.0f }, { 0.0f, 0.7f, 0.7f }, { 0.0f, 1.0f, 0.0f }, { 0.7f, 0.7f, 0.0f }, { 0.7f, 0.0f, 0.7f },
{ 0.0f, 0.0f, 1.0f }, { 0.7f, 0.0f, 0.7f }, { 0.7f, 0.7f, 0.0f }, { 0.0f, 1.0f, 0.0f }, { 0.0f, 0.7f, 0.7f }, { 1.0f, 0.0f, 0.0f } };
// Routine to create a scene graph representing a dodecahedron
SoSeparator
makeStellatedDodecahedron()
{
SoSeparator result = new SoSeparator();
// Using the new SoVertexProperty node is more efficient
SoVertexProperty myVertexProperty = new SoVertexProperty();
// Define colors for the faces
for ( int i = 0; i < 12; i++ )
myVertexProperty.orderedRGBA.set1Value( i, new SbColor( colors[i][0], colors[i][1], colors[i][2] ).getPackedValue() );
myVertexProperty.materialBinding.setValue( SoMaterialBinding.Bindings.PER_FACE );
// Define coordinates for vertices
myVertexProperty.vertex.setValues( 0, 12, vertexPositions );
// Define the IndexedFaceSet, with indices into
// the vertices:
SoIndexedFaceSet myFaceSet = new SoIndexedFaceSet();
myFaceSet.coordIndex.setValues( 0, indices );
myFaceSet.vertexProperty.setValue( myVertexProperty );
result.addChild( myFaceSet );
return result;
}
Polygons with Holes
Polygons with holes can be described efficiently as a set of “contours” (boundary edges) in SoFaceSet and SoIndexedFaceSet. The SoShapeHints windingType field allows you to specify how the interior and exterior regions of a polygon are determined. These classes expose the full power of the GLU tessellator.
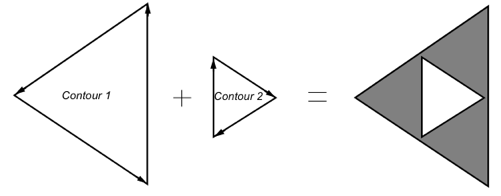
Polygon with hole
Basic Concepts
There are some basic concepts that you must know before creating holes with SoIndexedFaceSet or SoFaceSet shapes. Most important, to create a hole in a surface, you must insert an SoShapeHints node before the SoIndexedFaceSet or the SoFaceSet node.
 The windingType field of SoShapeHints was introduced in Open Inventor 4.0. If you specify a
The windingType field of SoShapeHints was introduced in Open Inventor 4.0. If you specify a
non-default value for the windingType field, when this node
is written to an Inventor file, the file will contain this new field. Older versions of Open
Inventor (before version 4.0) will not be able to read this file and will generate an Inventor
read error (unknown field).
Winding Numbers
For a single contour, the winding number of a point is the signed number of revolutions we make around that point while traveling once around the contour (where a counterclockwise revolution is positive and a clockwise revolution is negative). When there are several contours, the individual winding numbers are summed. In the following picture on the left, all three contours are counterclockwise, so each nested interior region adds one to the winding number.
In the picture on the right, the two interior contours are drawn clockwise, so the winding number decreases and actually becomes negative.
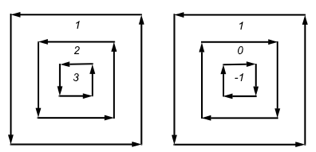
Winding numbers for sample contour
winding type to produce the desired results.
Winding type
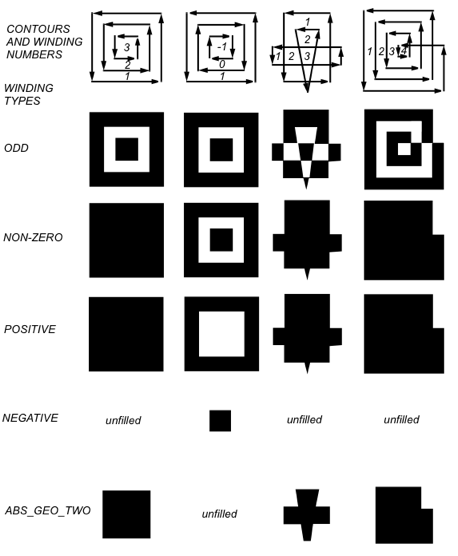
How winding rules define interiors
belongs to the chosen category.
We must add code (before the SoIndexedFaceSet or SoFaceSet ) to specify the winding type we want to use. For example,
C++ :
m_hints = new SoShapeHints;
root->addChild( m_hints );
// If we want to use an ODD winding type.
m_hints->windingType = SoShapeHints::ODD_TYPE;
C# :
SoShapeHints m_hints = new SoShapeHints();
root.AddChild( m_hints );
// If we want to use an ODD winding type.
m_hints.windingType.SetValue( ( int )SoShapeHints.WindingTypes.ODD_TYPE );
Java :
SoShapeHints m_hints = new SoShapeHints();
root.addChild( m_hints );
// If we want to use an ODD winding type.
m_hints.windingType.setValue( SoShapeHints.WindingTypes.ODD_TYPE );
Now, we must integrate this code with the SoIndexedFaceSet or the SoFaceSet shapes.
Create a Hole in a Face with SoIndexedFaceSet
- Create a list of coordinates for the contours you will use. (See SoIndexedFaceSet in the Reference Manual.)
Example:
C++ :
static const float vertexPositions[7][3] = { { 0, 0, 0 }, { 1, 1, 0 }, { 1, 0, 0 }, { 1, -1, 0 },
{ 0.3f, 0.2f, 0 }, { 0.8f, 0, 0 }, { 0.3f, -0.2f, 0 } };
C# :
static const float[, ] vertexPositions =
new float[7, 3]{ { 0, 0, 0 }, { 1, 1, 0 }, { 1, 0, 0 }, { 1, -1, 0 }, { 0.3f, 0.2f, 0 }, { 0.8f, 0, 0 }, { 0.3f, -0.2f, 0 } };
Java :
static float[][] vertexPositions =
new float[][]{ { 0, 0, 0 }, { 1, 1, 0 }, { 1, 0, 0 }, { 1, -1, 0 }, { 0.3f, 0.2f, 0 }, { 0.8f, 0, 0 }, { 0.3f, -0.2f, 0 } };
- Now we define indices for the outer contour and the contour that will define the hole.
Example:
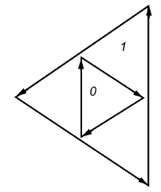
Winding numbers defining a hole
static int32_t indices[8] = {
0, 3, 1, SO_END_CONTOUR_INDEX, // Outer contour
5, 6, 4, SO_END_CONTOUR_INDEX // Hole contour
};
C# :
public static int[] indices = new int[8]{
0, 3, 1, -1, // Outer contour
5, 6, 4, -1 // Hole contour
};
Java :
public static int[] indices = new int[]{
0, 3, 1, -1, // Outer contour
5, 6, 4, -1 // Hole contour
};
Winding numbers defining a hole shows the winding numbers for the different regions of the polygon (see the section called “Winding Numbers”). The centermost region has a winding number of 0 because the first contour is counterclockwise, and the interior one is clockwise.
As you can see, we have defined two contours. The first one is the outer contour and the second one is the definition of the hole.
 You can define more than one hole in a face: The following is the skeleton of a list of contours:C++ :
You can define more than one hole in a face: The following is the skeleton of a list of contours:C++ :
// First contour of the polygon with hole<br/><list of indices>,SO_END_CONTOUR_INDEX,// Second contour of the polygon with hole<br/><list of
// indices>,SO_END_CONTOUR_INDEX,// Third contour of the polygon with hole<br/><list of indices>,SO_END_CONTOUR_INDEX<br/>...
C# :
Java :
This list of contours defines a set of regions, any of which may define
a hole depending on the winding numbers and the winding type.
 It is also possible to define multiple faces, each of which has
It is also possible to define multiple faces, each of which has
multiple contours. For example:C++ :
// First contour of the polygon with hole<br/><list of indices>,SO_END_CONTOUR_INDEX,// Second contour of the polygon with hole<br/><list of
// indices>,SO_END_CONTOUR_INDEX,<br/>...// Last contour of the block and end of the block.<br/><list of indices>,SO_END_POLYGON_INDEX<br/>//
// Beginning of the new block of contour.// First contour of the polygon with hole<br/><list of indices>,SO_END_CONTOUR_INDEX,// Second contour of the
// polygon with hole<br/><list of indices>,SO_END_CONTOUR_INDEX,<br/>...// Last contour of the block and end of the block.<br/><list of
// indices>,SO_END_POLYGON_INDEX<br/>...
C# :
Java :
- Now we have to decide what winding type we are going to use (see the section called “Winding type”):
,_NON_ZERO,_and_POSITIVE_winding_types
ODD, NON_ZERO, and POSITIVE winding types
* For ODD, NON_ZERO, and POSITIVE: See @ref ODD,_NON_ZERO,_and_POSITIVE_winding_types "ODD, NON_ZERO, and POSITIVE winding types" .
* For NEGATIVE and ABS_GEQ_TWO: Unfilled.
* For NO_WINDING: Two distinct but coplanar surfaces.To describe this in Open Inventor we must add the following code before the definition of the **SoIndexedFaceSet** :
C++ :
m_hints = new SoShapeHints;
root->addChild( m_hints );
// If we want to use an ODD winding type.
m_hints->windingType = SoShapeHints::ODD_TYPE;
C# :
SoShapeHints m_hints = new SoShapeHints();
root.AddChild( m_hints );
// If we want to use an ODD winding type.
m_hints.windingType.Value = SoShapeHints.WindingTypes.ODD_TYPE;
Java :
SoShapeHints m_hints = new SoShapeHints();
root.addChild( m_hints );
// If we want to use an ODD winding type.
m_hints.windingType.setValue( SoShapeHints.WindingTypes.ODD_TYPE );
 If we forget the previous four lines, we will get two coplanar sufaces. And now the final code will be:
If we forget the previous four lines, we will get two coplanar sufaces. And now the final code will be:
C++ :
SoSeparator* root = new SoSeparator;
root->ref();
// 1) Define the winding type to use. This code asks Open Inventor to
// use the following IndexedFaceSet as contours.
myShapeHints = new SoShapeHints;
root->addChild( myShapeHints );
// If we want to use an ODD winding type.
myShapeHints->windingType = SoShapeHints::ODD_TYPE;
// 2) Creation of the indexedFaceSet.
SoVertexProperty* myVertexProperty = new SoVertexProperty;
// Define coordinates for vertices
myVertexProperty->vertex.setValues( 0, 7, vertexPositions );
// Define the IndexedFaceSet, with indices into the vertices:
SoIndexedFaceSet* myIndexedFaceSet = new SoIndexedFaceSet;
myIndexedFaceSet->coordIndex.setValues( 0, 8, indices );
myIndexedFaceSet->vertexProperty.setValue( myVertexProperty );
root->addChild( myIndexedFaceSet );
C# :
SoSeparator root = new SoSeparator();
// 1) Define the winding type to use. This code asks Open Inventor to
// use the following IndexedFaceSet as contours.
SoShapeHints myShapeHints = new SoShapeHints();
root.AddChild( myShapeHints );
// If we want to use an ODD winding type.
myShapeHints.windingType.Value = SoShapeHints.WindingTypes.ODD_TYPE;
// 2) Creation of the indexedFaceSet.
SoVertexProperty myVertexProperty = new SoVertexProperty();
// Define coordinates for vertices
myVertexProperty.vertex.SetValues( 0, vertexPositions );
// Define the IndexedFaceSet, with indices into the vertices:
SoIndexedFaceSet myIndexedFaceSet = new SoIndexedFaceSet();
myIndexedFaceSet.coordIndex.SetValues( 0, indices );
myIndexedFaceSet.vertexProperty.Value = myVertexProperty;
root.AddChild( myIndexedFaceSet );
Java :
SoSeparator root = new SoSeparator();
// 1) Define the winding type to use. This code asks Open Inventor to
// use the following IndexedFaceSet as contours.
SoShapeHints myShapeHints = new SoShapeHints();
root.addChild( myShapeHints );
// If we want to use an ODD winding type.
myShapeHints.windingType.setValue( SoShapeHints.WindingTypes.ODD_TYPE );
// 2) Creation of the indexedFaceSet.
SoVertexProperty myVertexProperty = new SoVertexProperty();
// Define coordinates for vertices
myVertexProperty.vertex.setValues( 0, vertexPositions );
// Define the IndexedFaceSet, with indices into the vertices:
SoIndexedFaceSet myIndexedFaceSet = new SoIndexedFaceSet();
myIndexedFaceSet.coordIndex.setValues( 0, indices );
myIndexedFaceSet.vertexProperty.setValue( myVertexProperty );
root.addChild( myIndexedFaceSet );
Create a Hole in a Face with SoFaceSet
With the SoFaceSet node, there are no indices. It uses the coordinates in order, starting with the first one. Each contour has a number of vertices specified by a value in the numVertices field.
Example:
C++ :
static const float vertices[6][3] = {
// First contour.
{ 0, 0, 0 },
{ 1, -1, 0 },
{ 1, 1, 0 },
// Second contour.
{ 0.8f, 0, 0 },
{ 0.3f, -0.2f, 0 },
{ 0.3f, 0.2f, 0 }
};
// Number of vertices in each polygon:
static int32_t numvertices[2] = { 3, 3 };
C# :
static const float[, ] vertices = new float[6, 3]{ // First contour.
{ 0, 0, 0 },
{ 1, -1, 0 },
{ 1, 1, 0 },
// Second contour.
{ 0.8f, 0, 0 },
{ 0.3f, -0.2f, 0 },
{ 0.3f, 0.2f, 0 }
};
// Number of vertices in each polygon:
static int[] numvertices = new int[2]{ 3, 3 };
Java :
static float[][] vertices = new float[][]{ // First contour.
{ 0, 0, 0 },
{ 1, -1, 0 },
{ 1, 1, 0 },
// Second contour.
{ 0.8f, 0, 0 },
{ 0.3f, -0.2f, 0 },
{ 0.3f, 0.2f, 0 }
};
// Number of vertices in each polygon:
static int[] numvertices = new int[]{ 3, 3 };
Just like the previous example, the winding numbers are shown in Winding numbers defining a hole .
Now we must specify the winding type to use (See the section called “Winding type”), which is given by the following code:
C++ :
m_hints = new SoShapeHints;
root->addChild( m_hints );
// If we want to use an ODD winding type.
m_hints->windingType = SoShapeHints::ODD_TYPE;
C# :
SoShapeHints m_hints = new SoShapeHints();
root.AddChild( m_hints );
// If we want to use an ODD winding type.
m_hints.windingType.Value = SoShapeHints.WindingTypes.ODD_TYPE;
Java :
SoShapeHints m_hints = new SoShapeHints();
root.addChild( m_hints );
// If we want to use an ODD winding type.
m_hints.windingType.setValue( SoShapeHints.WindingTypes.ODD_TYPE );
 If we forget the previous four lines, we will get get two coplanar
If we forget the previous four lines, we will get get two coplanar
sufaces.
Here are results we will get in our example with following winding types:
- For ODD, NON_ZERO, and POSITIVE: See ODD,_NON_ZERO,_and_POSITIVE_winding_types "ODD, NON_ZERO, and POSITIVE winding types" .
- For NEGATIVE and ABS_GEQ_TWO: Unfilled.
- For NO_WINDING: Two distinct (but coplanar) faces. The final code to create a hole with an SoFaceSet node is:
C++ :
SoSeparator* root = new SoSeparator;
root->ref();
// 1) Define the winding type to use. This code asks Open Inventor to
// use following IndexedFaceSet as contours.
myShapeHints = new SoShapeHints;
root->addChild( myShapeHints );
// If we want to use an ODD winding type.
myShapeHints->windingType = SoShapeHints::ODD_TYPE;
// 2) Create the SoFaceSet
// Using the new SoVertexProperty node is more efficient
SoVertexProperty* myVertexProperty = new SoVertexProperty;
// Define coordinates for vertices
myVertexProperty->vertex.setValues( 0, 12, vertices );
// Define the FaceSet
SoFaceSet* myFaceSet = new SoFaceSet;
myFaceSet->numVertices.setValues( 0, 4, numvertices );
myFaceSet->vertexProperty.setValue( myVertexProperty );
root->addChild( myFaceSet );
C# :
SoSeparator root = new SoSeparator();
// 1) Define the winding type to use. This code asks Open Inventor to
// use following IndexedFaceSet as contours.
SoShapeHints myShapeHints = new SoShapeHints();
root.AddChild( myShapeHints );
// If we want to use an ODD winding type.
myShapeHints.windingType.Value = SoShapeHints.WindingTypes.ODD_TYPE;
// 2) Create the SoFaceSet
// Using the new SoVertexProperty node is more efficient
SoVertexProperty myVertexProperty = new SoVertexProperty();
// Define coordinates for vertices
myVertexProperty.vertex.SetValues( 0, vertices );
// Define the FaceSet
SoFaceSet myFaceSet = new SoFaceSet();
myFaceSet.numVertices.SetValues( 0, numvertices );
myFaceSet.vertexProperty.Value = myVertexProperty;
root.AddChild( myFaceSet );
Java :
SoSeparator root = new SoSeparator();
// 1) Define the winding type to use. This code asks Open Inventor to
// use following IndexedFaceSet as contours.
SoShapeHints myShapeHints = new SoShapeHints();
root.addChild( myShapeHints );
// If we want to use an ODD winding type.
myShapeHints.windingType.setValue( SoShapeHints.WindingTypes.ODD_TYPE );
// 2) Create the SoFaceSet
// Using the new SoVertexProperty node is more efficient
SoVertexProperty myVertexProperty = new SoVertexProperty();
// Define coordinates for vertices
myVertexProperty.vertex.setValues( 0, vertices );
// Define the FaceSet
SoFaceSet myFaceSet = new SoFaceSet();
myFaceSet.numVertices.setValues( 0, numvertices );
myFaceSet.vertexProperty.setValue( myVertexProperty );
root.addChild( myFaceSet );
Triangle Strip Set
The SoTriangleStripSet node constructs triangle strips out of the vertices located at the current coordinates. It is one of the fastest ways to draw polygonal objects in Inventor. The triangle strip set uses the current coordinates, in order, starting at the index specified by the startIndex field. (If no index is specified, it starts at the first index.)
The numVertices field indicates the number of vertices to use for each triangle strip in the set. The triangle strip set is described as follows:
C++ :
static long numVertices[2] = {
32, // flag
8 // pole
};
SoTriangleStripSet* myStrips = new SoTriangleStripSet;
myStrips->numVertices.setValues( 0, 2, numVertices );
C# :
static int[] numVertices = new int[2]{
32, // flag
8 // pole
};
SoTriangleStripSet myStrips = new SoTriangleStripSet();
myStrips.numVertices.SetValues( 0, numVertices );
Java :
static int[] numVertices = new int[]{
32, // flag
8 // pole
};
SoTriangleStripSet myStrips = new SoTriangleStripSet();
myStrips.numVertices.setValues( 0, numVertices );
Because the numVertices field contains an array with two values, two triangle strips are created. The first strip (the flag) is made from the first 32 coordinate values. The second strip (the flagpole) is made from the next 8 coordinates. Face 0 determines the vertex ordering—in this case, counterclockwise.
 Triangle strip sets and quad meshes are generally faster to render than face sets.
Triangle strip sets and quad meshes are generally faster to render than face sets.
Creating a Triangle Strip Set shows the code for creating a pennant-shaped flag. Scene Graph for Triangle Strip Set Example shows the scene graph for this example. Triangle Strip Set Example shows the resulting image.
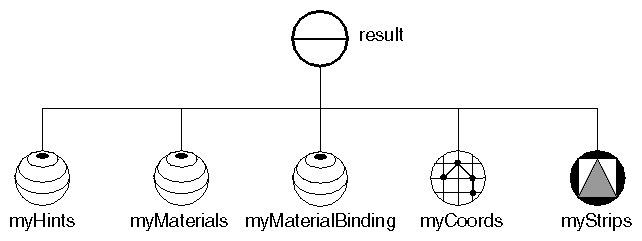
Scene Graph for Triangle Strip Set Example
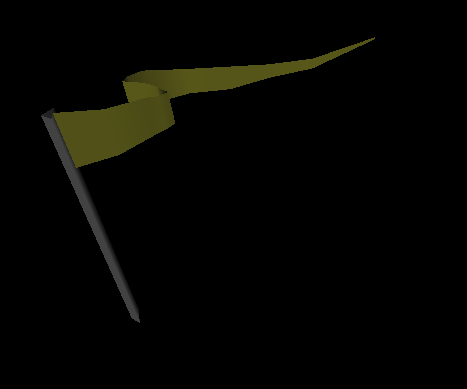
Triangle Strip Set Example
Creating a Triangle Strip Set
Example : Creating a Triangle Strip Set
C++ :
// Positions of all of the vertices:
static float vertexPositions[40][3] = {
{ 0, 12, 0 }, { 0, 15, 0 }, { 2.1, 12.1, -.2 }, { 2.1, 14.6, -.2 }, { 4, 12.5, -.7 }, { 4, 14.5, -.7 }, { 4.5, 12.6, -.8 },
{ 4.5, 14.4, -.8 }, { 5, 12.7, -1 }, { 5, 14.4, -1 }, { 4.5, 12.8, -1.4 }, { 4.5, 14.6, -1.4 }, { 4, 12.9, -1.6 }, { 4, 14.8, -1.6 },
{ 3.3, 12.9, -1.8 }, { 3.3, 14.9, -1.8 }, { 3, 13, -2.0 }, { 3, 14.9, -2.0 }, { 3.3, 13.1, -2.2 }, { 3.3, 15.0, -2.2 }, { 4, 13.2, -2.5 },
{ 4, 15.0, -2.5 }, { 6, 13.5, -2.2 }, { 6, 14.8, -2.2 }, { 8, 13.4, -2 }, { 8, 14.6, -2 }, { 10, 13.7, -1.8 }, { 10, 14.4, -1.8 },
{ 12, 14, -1.3 }, { 12, 14.5, -1.3 }, { 15, 14.9, -1.2 }, { 15, 15, -1.2 },
{ -.5, 15, 0 }, { -.5, 0, 0 }, // the flagpole
{ 0, 15, .5 }, { 0, 0, .5 }, { 0, 15, -.5 }, { 0, 0, -.5 }, { -.5, 15, 0 }, { -.5, 0, 0 }
};
// Number of vertices in each strip.
static long numVertices[2] = {
32, // flag
8 // pole
};
// Colors for the 12 faces
static float colors[2][3] = {
{ .5, .5, 1 }, // purple flag
{ .4, .4, .4 }, // grey flagpole
};
// Routine to create a scene graph representing a pennant.
SoSeparator*
makePennant()
{
SoSeparator* result = new SoSeparator;
result->ref();
// A shape hints tells the ordering of polygons.
// This ensures double-sided lighting.
SoShapeHints* myHints = new SoShapeHints;
myHints->vertexOrdering = SoShapeHints::COUNTERCLOCKWISE;
result->addChild( myHints );
// Define colors for the strips
SoMaterial* myMaterials = new SoMaterial;
myMaterials->diffuseColor.setValues( 0, 2, colors );
result->addChild( myMaterials );
SoMaterialBinding* myMaterialBinding = new SoMaterialBinding;
myMaterialBinding->value = SoMaterialBinding::PER_PART;
result->addChild( myMaterialBinding );
// Define coordinates for vertices
SoCoordinate3* myCoords = new SoCoordinate3;
myCoords->point.setValues( 0, 40, vertexPositions );
result->addChild( myCoords );
// Define the TriangleStripSet, made of two strips.
SoTriangleStripSet* myStrips = new SoTriangleStripSet;
myStrips->numVertices.setValues( 0, 2, numVertices );
result->addChild( myStrips );
result->unrefNoDelete();
return result;
}
C# :
// Positions of all of the vertices:
float[, ] vertexPositions =
new float[40, 3]{ { 0.0f, 12.0f, 0.0f }, { 0.0f, 15.0f, 0.0f }, { 2.1f, 12.1f, -0.2f }, { 2.1f, 14.6f, -0.2f }, { 4.0f, 12.5f, -0.7f },
{ 4.0f, 14.5f, -0.7f }, { 4.5f, 12.6f, -0.8f }, { 4.5f, 14.4f, -0.8f }, { 5.0f, 12.7f, -1.0f }, { 5.0f, 14.4f, -1.0f },
{ 4.5f, 12.8f, -1.4f }, { 4.5f, 14.6f, -1.4f }, { 4.0f, 12.9f, -1.6f }, { 4.0f, 14.8f, -1.6f }, { 3.3f, 12.9f, -1.8f },
{ 3.3f, 14.9f, -1.8f }, { 3.0f, 13.0f, -2.0f }, { 3.0f, 14.9f, -2.0f }, { 3.3f, 13.1f, -2.2f }, { 3.3f, 15.0f, -2.2f },
{ 4.0f, 13.2f, -2.5f }, { 4.0f, 15.0f, -2.5f }, { 6.0f, 13.5f, -2.2f }, { 6.0f, 14.8f, -2.2f }, { 8.0f, 13.4f, -2.0f },
{ 8.0f, 14.6f, -2.0f }, { 10.0f, 13.7f, -1.8f }, { 10.0f, 14.4f, -1.8f }, { 12.0f, 14.0f, -1.3f }, { 12.0f, 14.5f, -1.3f },
{ 15.0f, 14.9f, -1.2f }, { 15.0f, 15.0f, -1.2f },
{ -0.5f, 15.0f, 0.0f }, { -0.5f, 0.0f, 0.0f }, // the flagpole
{ 0.0f, 15.0f, 0.5f }, { 0.0f, 0.0f, 0.5f }, { 0.0f, 15.0f, -0.5f }, { 0.0f, 0.0f, -0.5f }, { -0.5f, 15.0f, 0.0f },
{ -0.5f, 0.0f, 0.0f } };
// Number of vertices in each strip.
Int32[] numVertices = new Int32[2]{
32, // flag
8 // pole
};
// Colors for the 12 faces
float[, ] colors = new float[2, 3]{
{ 0.5f, 0.5f, 1.0f }, // purple flag
{ 0.4f, 0.4f, 0.4f }, // grey flagpole
};
// Routine to create a scene graph representing a pennant.
SoSeparator
MakePennant()
{
SoSeparator result = new SoSeparator();
// A shape hints tells the ordering of polygons.
// This insures double sided lighting.
SoShapeHints myHints = new SoShapeHints();
myHints.vertexOrdering.Value = SoShapeHints.VertexOrderings.COUNTERCLOCKWISE;
result.AddChild( myHints );
// Using the new SoVertexProperty node is more efficient
SoVertexProperty myVertexProperty = new SoVertexProperty();
// Define colors for the strips
for ( int i = 0; i < 2; i++ )
myVertexProperty.orderedRGBA[i] = new SbColor( colors[ i, 0 ], colors[ i, 1 ], colors[ i, 2 ] ).GetPackedValue();
myVertexProperty.materialBinding.Value = SoMaterialBinding.Bindings.PER_PART;
// Define coordinates for vertices
myVertexProperty.vertex.SetValues( 0, 40, vertexPositions );
// Define the TriangleStripSet, made of two strips.
SoTriangleStripSet myStrips = new SoTriangleStripSet();
myStrips.numVertices.SetValues( 0, numVertices );
myStrips.vertexProperty.Value = myVertexProperty;
result.AddChild( myStrips );
return result;
}
Java :
// Positions of all of the vertices:
static float vertexPositions[][] = {
{ 0F, 12F, 0F }, { 0F, 15F, 0F }, { 2.1F, 12.1F, -.2F }, { 2.1F, 14.6F, -.2F }, { 4F, 12.5F, -.7F }, { 4F, 14.5F, -.7F },
{ 4.5F, 12.6F, -.8F }, { 4.5F, 14.4F, -.8F }, { 5F, 12.7F, -1F }, { 5F, 14.4F, -1F }, { 4.5F, 12.8F, -1.4F }, { 4.5F, 14.6F, -1.4F },
{ 4F, 12.9F, -1.6F }, { 4F, 14.8F, -1.6F }, { 3.3F, 12.9F, -1.8F }, { 3.3F, 14.9F, -1.8F }, { 3F, 13F, -2.0F }, { 3F, 14.9F, -2.0F },
{ 3.3F, 13.1F, -2.2F }, { 3.3F, 15.0F, -2.2F }, { 4F, 13.2F, -2.5F }, { 4F, 15.0F, -2.5F }, { 6F, 13.5F, -2.2F }, { 6F, 14.8F, -2.2F },
{ 8F, 13.4F, -2F }, { 8F, 14.6F, -2F }, { 10F, 13.7F, -1.8F }, { 10F, 14.4F, -1.8F }, { 12F, 14F, -1.3F }, { 12F, 14.5F, -1.3F },
{ 15F, 14.9F, -1.2F }, { 15F, 15F, -1.2F },
{ -.5F, 15F, 0F }, { -.5F, 0F, 0F }, // the flagpole
{ 0F, 15F, .5F }, { 0F, 0F, .5F }, { 0F, 15F, -.5F }, { 0F, 0F, -.5F }, { -.5F, 15F, 0F }, { -.5F, 0F, 0F }
};
// Number of vertices in each strip.
static int numVertices[] = {
32, // flag
8 // pole
};
// Colors for the 12 faces
static float colors[][] = {
{ .5F, .5F, 1F }, // purple flag
{ .4F, .4F, .4F } // grey flagpole
};
// Routine to create a scene graph representing a pennant.
SoSeparator
makePennant()
{
SoSeparator result = new SoSeparator();
// A shape hints tells the ordering of polygons.
// This insures double sided lighting.
SoShapeHints myHints = new SoShapeHints();
myHints.vertexOrdering.setValue( SoShapeHints.VertexOrderings.COUNTERCLOCKWISE );
result.addChild( myHints );
// This is the preferred code for Inventor 2.1
// otherwise, see below the commented block
// Using the new SoVertexProperty node is more efficient
SoVertexProperty myVertexProperty = new SoVertexProperty();
// Define colors for the strips
for ( int i = 0; i < 2; i++ )
myVertexProperty.orderedRGBA.set1Value( i, new SbColor( colors[i] ).getPackedValue() );
myVertexProperty.materialBinding.setValue( SoMaterialBinding.Bindings.PER_PART );
// Define coordinates for vertices
myVertexProperty.vertex.setValues( 0, vertexPositions );
// Define the TriangleStripSet, made of two strips.
SoTriangleStripSet myStrips = new SoTriangleStripSet();
myStrips.numVertices.setValues( 0, numVertices );
myStrips.vertexProperty.setValue( myVertexProperty );
result.addChild( myStrips );
return result;
}
Quad Mesh
The SoQuadMesh node constructs quadrilaterals from the vertices located at the current coordinates. It uses the coordinates in order, starting at the index specified by the startIndex field. (If no index is specified, it starts at the first index.)
The verticesPerColumn and verticesPerRow fields indicate the number of vertices in the columns and rows of the mesh. Creating a Quad Mesh creates a quad mesh as follows:
C++ :
SoQuadMesh* myQuadMesh = new SoQuadMesh;
myQuadMesh->verticesPerRow = 12;
myQuadMesh->verticesPerColumn = 5;
C# :
SoQuadMesh myQuadMesh = new SoQuadMesh();
myQuadMesh.verticesPerRow.Value = 12;
myQuadMesh.verticesPerColumn.Value = 5;
Java :
SoQuadMesh myQuadMesh = new SoQuadMesh();
myQuadMesh.verticesPerRow.setValue( 12 );
myQuadMesh.verticesPerColumn.setValue( 5 );
Each row in this quad mesh contains 12 vertices. Each column contains 5 vertices. Scene Graph for Quad Mesh Example shows the scene graph for this example. Quad Mesh Example shows the resulting image.
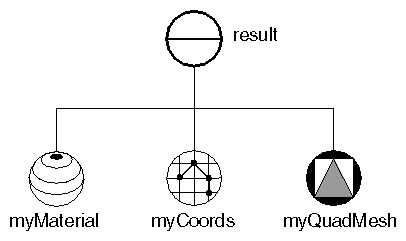
Scene Graph for Quad Mesh Example
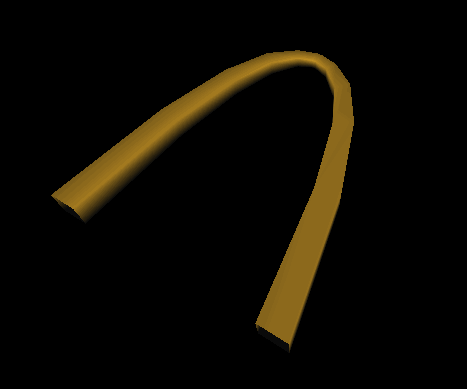
Quad Mesh Example
Creating a Quad Mesh
Example : Creating a Quad Mesh
C++ :
// Positions of all of the vertices:
static float vertexPositions[160][3] = { // 1st row
{ -13.0, 0.0, 1.5 },
{ -10.3, 13.7, 1.2 },
{ -7.6, 21.7, 1.0 },
{ -5.0, 26.1, 0.8 },
{ -2.3, 28.2, 0.6 },
{ -0.3, 28.8, 0.5 },
{ 0.3, 28.8, 0.5 },
{ 2.3, 28.2, 0.6 },
{ 5.0, 26.1, 0.8 },
{ 7.6, 21.7, 1.0 },
{ 10.3, 13.7, 1.2 },
{ 13.0, 0.0, 1.5 },
// 2nd row
{ -10.0, 0.0, 1.5 },
{ -7.9, 13.2, 1.2 },
{ -5.8, 20.8, 1.0 },
{ -3.8, 25.0, 0.8 },
{ -1.7, 27.1, 0.6 },
{ -0.2, 27.6, 0.5 },
{ 0.2, 27.6, 0.5 },
{ 1.7, 27.1, 0.6 },
{ 3.8, 25.0, 0.8 },
{ 5.8, 20.8, 1.0 },
{ 7.9, 13.2, 1.2 },
{ 10.0, 0.0, 1.5 },
// 3rd row
{ -10.0, 0.0, -1.5 },
{ -7.9, 13.2, -1.2 },
{ -5.8, 20.8, -1.0 },
{ -3.8, 25.0, -0.8 },
{ -1.7, 27.1, -0.6 },
{ -0.2, 27.6, -0.5 },
{ 0.2, 27.6, -0.5 },
{ 1.7, 27.1, -0.6 },
{ 3.8, 25.0, -0.8 },
{ 5.8, 20.8, -1.0 },
{ 7.9, 13.2, -1.2 },
{ 10.0, 0.0, -1.5 },
// 4th row
{ -13.0, 0.0, -1.5 },
{ -10.3, 13.7, -1.2 },
{ -7.6, 21.7, -1.0 },
{ -5.0, 26.1, -0.8 },
{ -2.3, 28.2, -0.6 },
{ -0.3, 28.8, -0.5 },
{ 0.3, 28.8, -0.5 },
{ 2.3, 28.2, -0.6 },
{ 5.0, 26.1, -0.8 },
{ 7.6, 21.7, -1.0 },
{ 10.3, 13.7, -1.2 },
{ 13.0, 0.0, -1.5 },
// 5th row
{ -13.0, 0.0, 1.5 },
{ -10.3, 13.7, 1.2 },
{ -7.6, 21.7, 1.0 },
{ -5.0, 26.1, 0.8 },
{ -2.3, 28.2, 0.6 },
{ -0.3, 28.8, 0.5 },
{ 0.3, 28.8, 0.5 },
{ 2.3, 28.2, 0.6 },
{ 5.0, 26.1, 0.8 },
{ 7.6, 21.7, 1.0 },
{ 10.3, 13.7, 1.2 },
{ 13.0, 0.0, 1.5 }
};
// Routine to create a scene graph representing an arch.
SoSeparator*
makeArch()
{
SoSeparator* result = new SoSeparator;
result->ref();
// Define the material
SoMaterial* myMaterial = new SoMaterial;
myMaterial->diffuseColor.setValue( .78, .57, .11 );
result->addChild( myMaterial );
// Define coordinates for vertices
SoCoordinate3* myCoords = new SoCoordinate3;
myCoords->point.setValues( 0, 60, vertexPositions );
result->addChild( myCoords );
// Define the QuadMesh.
SoQuadMesh* myQuadMesh = new SoQuadMesh;
myQuadMesh->verticesPerRow = 12;
myQuadMesh->verticesPerColumn = 5;
result->addChild( myQuadMesh );
result->unrefNoDelete();
return result;
}
C# :
// Positions of all of the vertices:
float[, ] vertexPositions = new float[60, 3]{ // 1st row
{ -13.0f, 0.0f, 1.5f },
{ -10.3f, 13.7f, 1.2f },
{ -7.6f, 21.7f, 1.0f },
{ -5.0f, 26.1f, 0.8f },
{ -2.3f, 28.2f, 0.6f },
{ -0.3f, 28.8f, 0.5f },
{ 0.3f, 28.8f, 0.5f },
{ 2.3f, 28.2f, 0.6f },
{ 5.0f, 26.1f, 0.8f },
{ 7.6f, 21.7f, 1.0f },
{ 10.3f, 13.7f, 1.2f },
{ 13.0f, 0.0f, 1.5f },
// 2nd row
{ -10.0f, 0.0f, 1.5f },
{ -7.9f, 13.2f, 1.2f },
{ -5.8f, 20.8f, 1.0f },
{ -3.8f, 25.0f, 0.8f },
{ -1.7f, 27.1f, 0.6f },
{ -0.2f, 27.6f, 0.5f },
{ 0.2f, 27.6f, 0.5f },
{ 1.7f, 27.1f, 0.6f },
{ 3.8f, 25.0f, 0.8f },
{ 5.8f, 20.8f, 1.0f },
{ 7.9f, 13.2f, 1.2f },
{ 10.0f, 0.0f, 1.5f },
// 3rd row
{ -10.0f, 0.0f, -1.5f },
{ -7.9f, 13.2f, -1.2f },
{ -5.8f, 20.8f, -1.0f },
{ -3.8f, 25.0f, -0.8f },
{ -1.7f, 27.1f, -0.6f },
{ -0.2f, 27.6f, -0.5f },
{ 0.2f, 27.6f, -0.5f },
{ 1.7f, 27.1f, -0.6f },
{ 3.8f, 25.0f, -0.8f },
{ 5.8f, 20.8f, -1.0f },
{ 7.9f, 13.2f, -1.2f },
{ 10.0f, 0.0f, -1.5f },
// 4th row
{ -13.0f, 0.0f, -1.5f },
{ -10.3f, 13.7f, -1.2f },
{ -7.6f, 21.7f, -1.0f },
{ -5.0f, 26.1f, -0.8f },
{ -2.3f, 28.2f, -0.6f },
{ -0.3f, 28.8f, -0.5f },
{ 0.3f, 28.8f, -0.5f },
{ 2.3f, 28.2f, -0.6f },
{ 5.0f, 26.1f, -0.8f },
{ 7.6f, 21.7f, -1.0f },
{ 10.3f, 13.7f, -1.2f },
{ 13.0f, 0.0f, -1.5f },
// 5th row
{ -13.0f, 0.0f, 1.5f },
{ -10.3f, 13.7f, 1.2f },
{ -7.6f, 21.7f, 1.0f },
{ -5.0f, 26.1f, 0.8f },
{ -2.3f, 28.2f, 0.6f },
{ -0.3f, 28.8f, 0.5f },
{ 0.3f, 28.8f, 0.5f },
{ 2.3f, 28.2f, 0.6f },
{ 5.0f, 26.1f, 0.8f },
{ 7.6f, 21.7f, 1.0f },
{ 10.3f, 13.7f, 1.2f },
{ 13.0f, 0.0f, 1.5f }
};
// Routine to create a scene graph representing an arch.
SoSeparator
MakeArch()
{
SoSeparator result = new SoSeparator();
// Using the new SoVertexProperty node is more efficient
SoVertexProperty myVertexProperty = new SoVertexProperty();
// Define the material
myVertexProperty.orderedRGBA.SetValue( new SbColor( 0.78f, 0.57f, 0.11f ).GetPackedValue() );
// Define coordinates for vertices
myVertexProperty.vertex.SetValues( 0, 60, vertexPositions );
// Define the QuadMesh.
SoQuadMesh myQuadMesh = new SoQuadMesh();
myQuadMesh.verticesPerRow.Value = 12;
myQuadMesh.verticesPerColumn.Value = 5;
myQuadMesh.vertexProperty.Value = myVertexProperty;
result.AddChild( myQuadMesh );
return result;
}
Java :
// Positions of all of the vertices:
static float vertexPositions[][] = {
// 1st row
{ -13.0F, 0.0F, 1.5F },
{ -10.3F, 13.7F, 1.2F },
{ -7.6F, 21.7F, 1.0F },
{ -5.0F, 26.1F, 0.8F },
{ -2.3F, 28.2F, 0.6F },
{ -0.3F, 28.8F, 0.5F },
{ 0.3F, 28.8F, 0.5F },
{ 2.3F, 28.2F, 0.6F },
{ 5.0F, 26.1F, 0.8F },
{ 7.6F, 21.7F, 1.0F },
{ 10.3F, 13.7F, 1.2F },
{ 13.0F, 0.0F, 1.5F },
// 2nd row
{ -10.0F, 0.0F, 1.5F },
{ -7.9F, 13.2F, 1.2F },
{ -5.8F, 20.8F, 1.0F },
{ -3.8F, 25.0F, 0.8F },
{ -1.7F, 27.1F, 0.6F },
{ -0.2F, 27.6F, 0.5F },
{ 0.2F, 27.6F, 0.5F },
{ 1.7F, 27.1F, 0.6F },
{ 3.8F, 25.0F, 0.8F },
{ 5.8F, 20.8F, 1.0F },
{ 7.9F, 13.2F, 1.2F },
{ 10.0F, 0.0F, 1.5F },
// 3rd row
{ -10.0F, 0.0F, -1.5F },
{ -7.9F, 13.2F, -1.2F },
{ -5.8F, 20.8F, -1.0F },
{ -3.8F, 25.0F, -0.8F },
{ -1.7F, 27.1F, -0.6F },
{ -0.2F, 27.6F, -0.5F },
{ 0.2F, 27.6F, -0.5F },
{ 1.7F, 27.1F, -0.6F },
{ 3.8F, 25.0F, -0.8F },
{ 5.8F, 20.8F, -1.0F },
{ 7.9F, 13.2F, -1.2F },
{ 10.0F, 0.0F, -1.5F },
// 4th row
{ -13.0F, 0.0F, -1.5F },
{ -10.3F, 13.7F, -1.2F },
{ -7.6F, 21.7F, -1.0F },
{ -5.0F, 26.1F, -0.8F },
{ -2.3F, 28.2F, -0.6F },
{ -0.3F, 28.8F, -0.5F },
{ 0.3F, 28.8F, -0.5F },
{ 2.3F, 28.2F, -0.6F },
{ 5.0F, 26.1F, -0.8F },
{ 7.6F, 21.7F, -1.0F },
{ 10.3F, 13.7F, -1.2F },
{ 13.0F, 0.0F, -1.5F },
// 5th row
{ -13.0F, 0.0F, 1.5F },
{ -10.3F, 13.7F, 1.2F },
{ -7.6F, 21.7F, 1.0F },
{ -5.0F, 26.1F, 0.8F },
{ -2.3F, 28.2F, 0.6F },
{ -0.3F, 28.8F, 0.5F },
{ 0.3F, 28.8F, 0.5F },
{ 2.3F, 28.2F, 0.6F },
{ 5.0F, 26.1F, 0.8F },
{ 7.6F, 21.7F, 1.0F },
{ 10.3F, 13.7F, 1.2F },
{ 13.0F, 0.0F, 1.5F }
};
// Routine to create a scene graph representing an arch.
SoSeparator
makeArch()
{
// This is the preferred code for Inventor 2.1
// otherwise, see below the commented block
// Using the new SoVertexProperty node is more efficient
SoVertexProperty myVertexProperty = new SoVertexProperty();
// Define the material
// myVertexProperty.orderedRGBA.setValue(
new SbColor(.78F, .57F, .11F).getPackedValue());
int rgb = new SbColor( .78F, .57F, .11F ).getPackedValue();
myVertexProperty.orderedRGBA.setValue( rgb );
// Define coordinates for vertices
myVertexProperty.vertex.setValues( 0, vertexPositions );
// Define the QuadMesh.
SoQuadMesh myQuadMesh = new SoQuadMesh();
myQuadMesh.verticesPerRow.setValue( 12 );
myQuadMesh.verticesPerColumn.setValue( 5 );
myQuadMesh.vertexProperty.setValue( myVertexProperty );
SoSeparator result = new SoSeparator();
result.addChild( myQuadMesh );
return result;
}

 Normals can also be generated automatically by Inventor, in which case you do not need an SoNormal node. See the section called “Generating Normals Automatically” for further information.
Normals can also be generated automatically by Inventor, in which case you do not need an SoNormal node. See the section called “Generating Normals Automatically” for further information.


 When you construct a scene graph, be sure that you have used as few nodes as possible to accomplish your goals. For example, to create a multifaceted polygonal shape, it's best to put all the coordinates for the shape into one SoCoordinate node and put the description of all the face sets into a single SoFaceSet (or SoIndexedFaceSet) node rather than using multiple nodes for each face.
When you construct a scene graph, be sure that you have used as few nodes as possible to accomplish your goals. For example, to create a multifaceted polygonal shape, it's best to put all the coordinates for the shape into one SoCoordinate node and put the description of all the face sets into a single SoFaceSet (or SoIndexedFaceSet) node rather than using multiple nodes for each face. If you use the SoShapeHints node to specify that the vertices are counterclockwise, you must specify the vertex indices according to the right-hand rule. The right-hand rule states that if you place the fingers of your right hand around the face following the direction in which the vertices are specified, your thumb points in the general direction of the geometric normal. Alternatively, you can specify the vertices in clockwise order. In this case, the direction of the geometric normal is determined by the left-hand rule.
If you use the SoShapeHints node to specify that the vertices are counterclockwise, you must specify the vertex indices according to the right-hand rule. The right-hand rule states that if you place the fingers of your right hand around the face following the direction in which the vertices are specified, your thumb points in the general direction of the geometric normal. Alternatively, you can specify the vertices in clockwise order. In this case, the direction of the geometric normal is determined by the left-hand rule.


 The windingType field of SoShapeHints was introduced in Open Inventor 4.0. If you specify a
The windingType field of SoShapeHints was introduced in Open Inventor 4.0. If you specify a


 You can define more than one hole in a face: The following is the skeleton of a list of contours:C++ :
You can define more than one hole in a face: The following is the skeleton of a list of contours:C++ :  It is also possible to define multiple faces, each of which has
It is also possible to define multiple faces, each of which has
 If we forget the previous four lines, we will get two coplanar sufaces. And now the final code will be:
If we forget the previous four lines, we will get two coplanar sufaces. And now the final code will be: If we forget the previous four lines, we will get get two coplanar
If we forget the previous four lines, we will get get two coplanar Triangle strip sets and quad meshes are generally faster to render than face sets.
Triangle strip sets and quad meshes are generally faster to render than face sets.